questionnaires assessed urinary function (IPSS), continence (ICS: 1–2),
and potency (IIEF-5) at months 6 and 12.
3.
Results
3.1.
Preoperative data
Clinical, pathologic, and biochemical preoperative data are
shown in
Table 1and Supplementary Table 1. Clinical stage
was T1c in all cases (normal digital rectal examination).
APC location and volume are shown in
Figure 2and
Supplementary Figure 1. In 11 of 17 cases (65%), tumor
extended up to the apical part of the gland.
3.2.
Perioperative results
Technique was feasible in all cases without open conversion
or intraoperative complications. After the first five
consecutive surgeries in an 18-mo period, there were no
transfusions, ICS score was
<
4 in all cases, and four of five
Table 1 – Clinical, pathologic, and biochemical preoperative data of the 17 patients included for anterior partial prostatectomy
Clinical
Age, yr, mean (IQR)
61 (54–66)
Preoperative PSA, ng/ml, median (IQR)
9.8 (7.1–11.3)
Biopsies
No. of cases with previous negative biopsy series,
n
(%)
11 (65)
No. of cases with cancer at 12 systematic posterior biopsies,
n
(%)
6 (35)
Maximum CCL at 12 systematic posterior biopsies, mm, median (IQR)
1 (1–2)
Maximum CCL at targeted biopsies, mm, median (IQR)
8 (7–9)
Gleason score,
n
6 (3 + 3)
8
7 (3 + 4)
8
7 (4 + 3)
1
MRI
Prostate volume, cm
3
, median (IQR)
45 (37–59)
Cancer volume, cm
3
, median (IQR)
4.15 (1.7–4.6)
*Tumor location,
n
Midline AFMS
11
Midline TZ/AFMS
2
Lateral TZ and AFMS
3
No visible lesion
1 *AFMS = anterior fibromuscular stroma; CCL = cancer core length; IQR = interquartile range; MRI = magnetic resonance imaging; PSA = prostate-specific antigen;
RP = radical prostatectomy; TZ = transition zone.
*
MRI was not suspicious for case 4, and cancer volume could not be calculated.
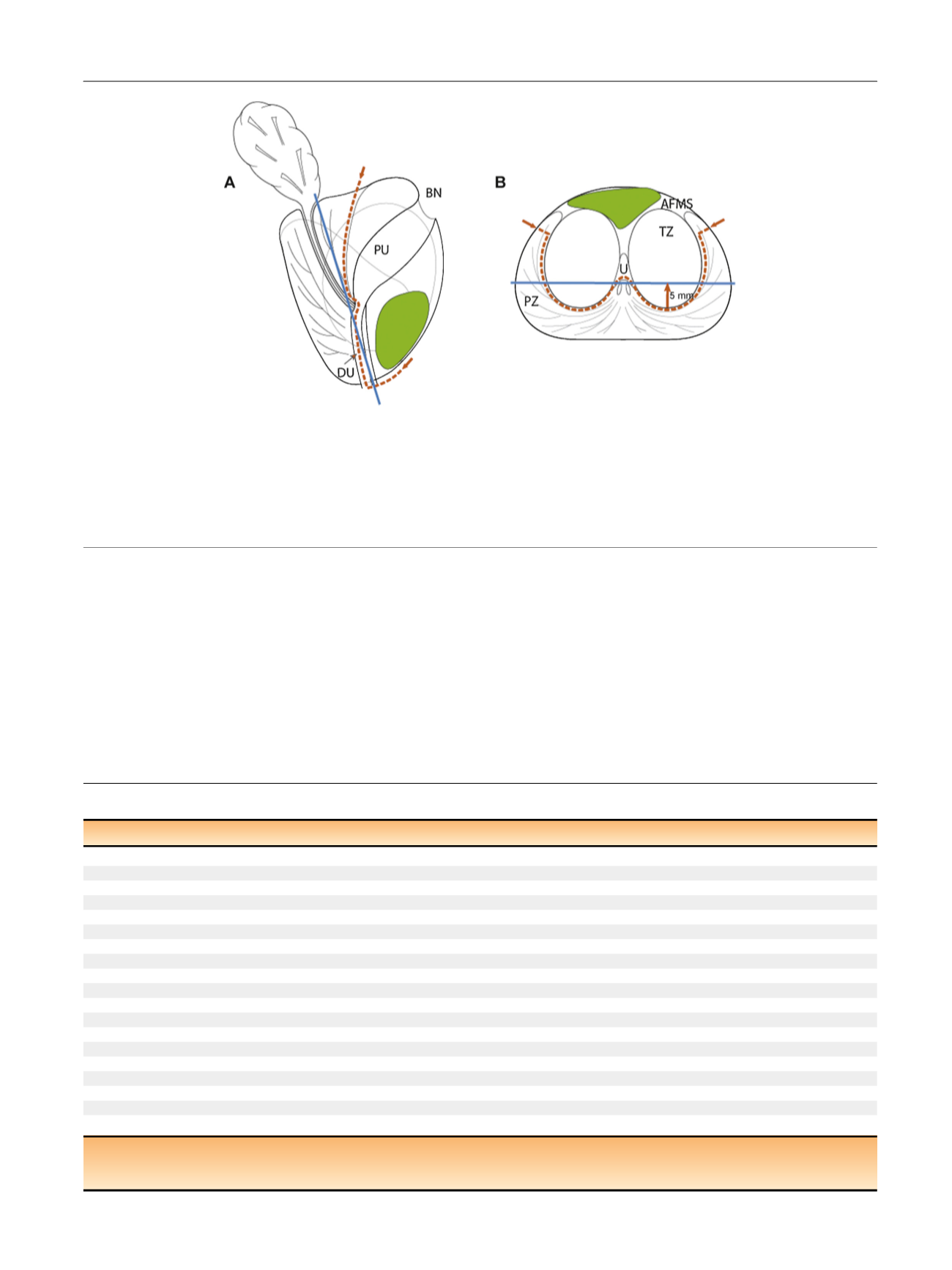
[(Fig._1)TD$FIG]
Fig. 1 – Schematic view of prostate (a) sagittal and (b) transverse aspects at midgland. Red dotted line shows dissection plane of anterior partial
prostatectomy. Protocol comprises en bloc template excision of the anterior part of the prostate including anterior fibromuscular stroma, prostate
adenoma (transition zone [TZ] and median lobe) with the proximal urethra, the anterior part of the distal (submontanal) urethra, the most anterior
apical parts of the peripheral zone, and anterior bladder neck. Blue line represents a coronal plane 5 mm (arrow) anterior to the posterior aspect of
the TZ. Average anterior cancer (in green) should be located at magnetic resonance imaging anterior to this coronal plane to ensure complete removal
during partial surgery.
AFMS = anterior fibromuscular stroma; BN = bladder neck; DU = distal urethra; PU = proximal urethra; PZ = peripheral zone; TZ = transition zone;
U = urethra.
E U R O P E A N U R O L O G Y 7 2 ( 2 0 1 7 ) 3 3 3 – 3 4 2
335