dissected. Medial and lateral limits consisted of the midline of the
inferior vena cava or aorta and the ureters, respectively. All nodal
packages were sent for pathologic evaluation according to their
anatomical location. At the end of the procedure the inferior vena cava,
the aorta, the inferior mesenteric artery, and the ureters were completely
skeletonized up to the renal vessels
( Fig. 5). Knee-length antiembolism
stockings and subcutaneous injections of low-molecular weight heparin
in the postoperative period were used for tromboprophylaxis.
2.3.
Covariates and outcomes
All patients had complete preoperative and pathologic data including
data on pathologic disease characteristics at RP, age at RASND, PSA at
RASND, time to BCR after RP, use of adjuvant and/or salvage therapies
after RP, and site and number of the positive PET/CT spots. Perioperative
outcomes consisted of operative time, blood loss, intraoperative
complications analyzed according to the Satava classification
[20] ,length of hospital stay (LoS), and 30-d postoperative complications
categorized according to the Clavien-Dindo classification
[21]. Patients
underwent follow-up visits every 3 mo during the 1st yr after surgery.
Biochemical response (BR) was defined as a PSA
<
0.2 ng/ml at 40 d after
RASND. Medians and interquartile ranges were reported for non-
normally distributed continuous variables. Frequencies and proportions
were reported for categorical variables.
3.
Results
3.1.
Baseline characteristics
Table 1depicts the demographic and tumor characteristics
of the study cohort. Median age at surgery was 66 yr.
Overall, four (25%) and seven (43.8%) patients had positive
surgical margins and pathologic Gleason score 8–10 at RP,
respectively. Overall, 13 (81.2%) patients received a pelvic
lymph node dissection during RP. The median number of
nodes removed was 19.5. Overall, seven (43.8%) patients
[(Fig._4)TD$FIG]
Fig. 4 – During retroperitoneal robot-assisted salvage nodal dissection
the inferior mesenteric artery was identified and isolated.
[(Fig._5)TD$FIG]
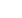
Fig. 5 – The cranial limit of the retroperitoneal robot-assisted salvage
nodal dissection consisted of the renal vessels.
[(Fig._3)TD$FIG]
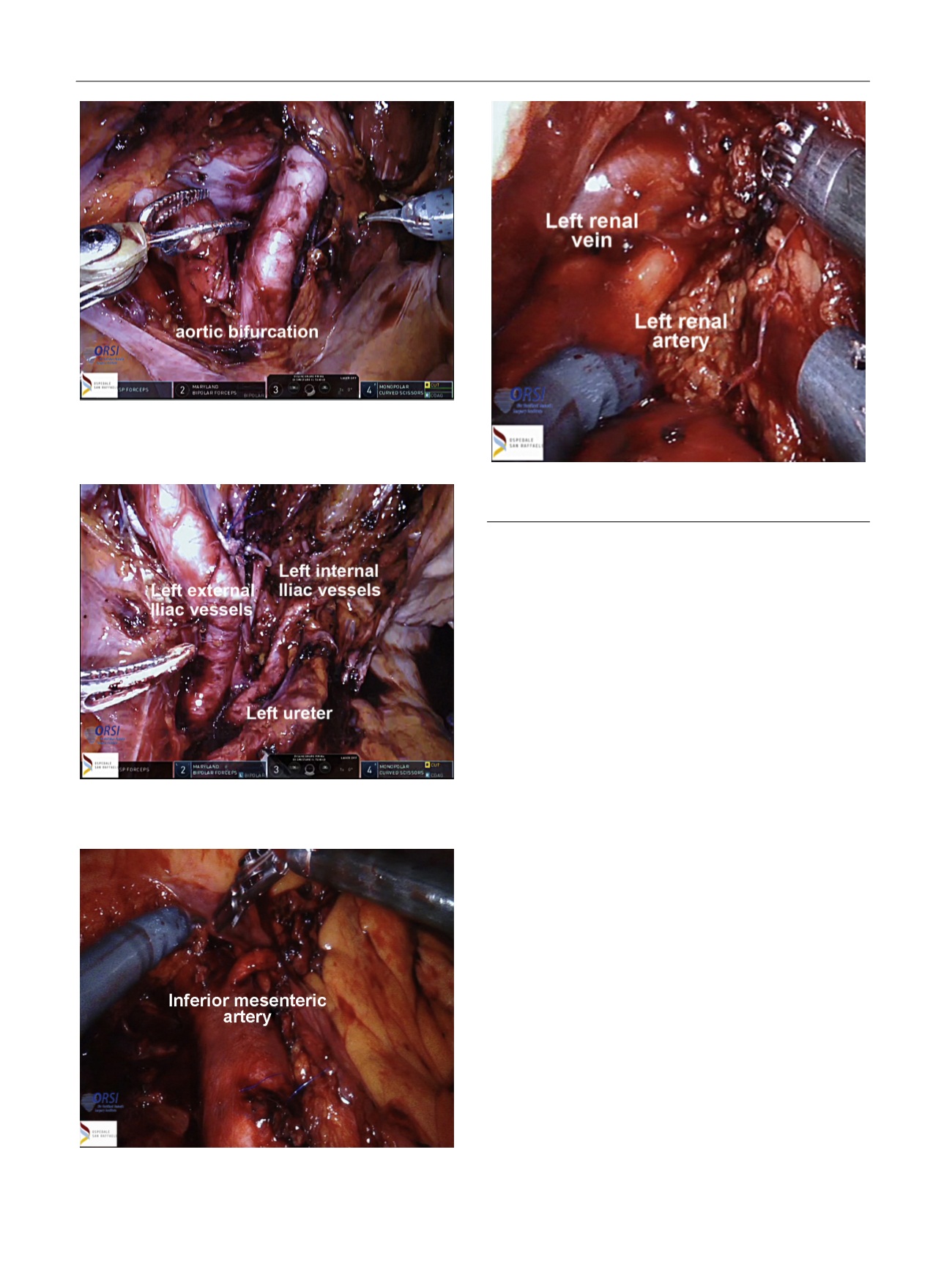
Fig. 3 – At the end of the pelvic nodal dissection the ureters and the iliac
vessels were completely skeletonized.
[(Fig._2)TD$FIG]
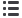
Fig. 2 – Robot-assisted salvage nodal dissection proximally included
removal of all lymph nodes along common iliac vessels up to the aortic
bifurcation.
E U R O P E A N U R O L O G Y 7 2 ( 2 0 1 7 ) 4 3 2 – 4 3 8
434